Do You Have Leaky Gut?
Leaky gut, also known as intestinal permeability, is a lot more common than most people think. Studies have shown that this afflicts more than 50% of the population, and it drives chronic disease.

When leaky gut is present, the immune system ramps up its response at the mucosal level and this increases inflammation and it weakens the gut barrier, which causes intact particles to leak through the gut junctions and into the blood stream.
The immune system will then respond, by further increasing inflammation, and signaling the brain that there is an issue.
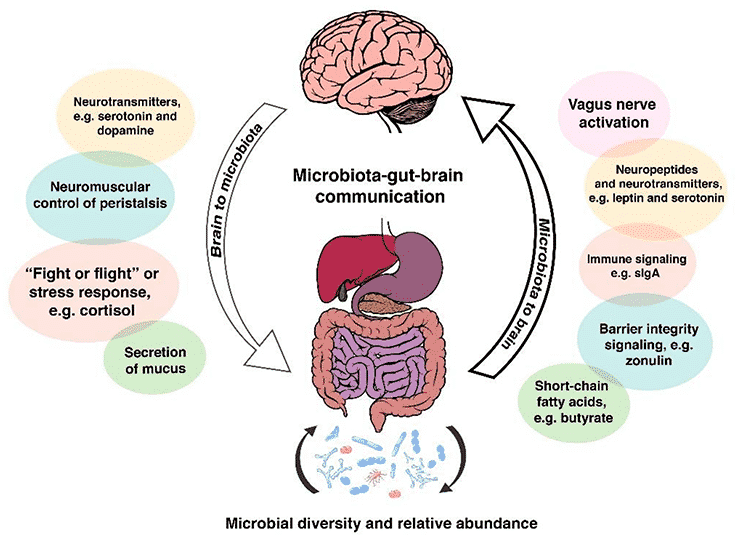
With good microbial diversity and abundance, and a healthy balanced intestinal tract, we see good short chain fatty acid production (fuels the gut lining), barrier integrity (normal tight junctions), balanced immune signaling (Secretory IgA, the immunoglobulin secreted by the cells that line your intestinal tract), good neuropeptides and neurotransmitters are produced and vagus nerve signaling.
The brain is responsible for producing neurotransmitters, neuromuscular control of peristalsis (motility), controlling fight or flight/ stress response and secretion of mucous.
When leaky gut is present – all of these pathways are disrupted. This creates a negative feedback loop, where the brain will send cytokines (inflammatory immune chemicals) to further increase inflammation and immune system involvement. Leaky gut can also cause leaky brain, where inflammatory reactions disrupt the blood brain barrier becomes permeable, causing brain fog, anxiety, and concentration issues.
The inflammation that is caused by leaky gut, does not stay local. Systemic inflammation can be triggered when the endotoxin LPS (lipopolysaccharide) leaches into the blood stream. LPS is the major component of the membrane in gram-negative bacteria. When these turn over in the intestinal tract (as bacteria do – they have a short lifespan), they dump LPS into the intestinal tract. If you have dysbiosis (imbalanced gut bacteria) and too many gram negative bacteria to begin with, LPS alone can drive leaky gut. Normally, LPS is dealt with within the intestinal lumen and some is directed to the liver, where the liver processes it out of the body. When LPS leaks over into the blood stream at high numbers, this will cause systemic inflammation.
Most practitioners, when presented with a patient with chronic gut symptoms, assume that leaky gut is present. I prefer to test for this. If identified, and if present, this is a PRIMARY target. We need to treat this directly and then we can test this again to make sure that it has healed.
We also need to identify why leaky gut is present.
Common causes of leaky gut:
- Acute/ Chronic Stress and:
- Parasites
- Antibiotics
- Dysbiosis/ Pathogens
- Mycotoxins
- Chemicals/ Toxin Load
Nutritional Therapies That Can Help to Address Intestinal Permeability
- Zinc carnosine
- L-glutamine
- Curcumin
- L-arginine
- N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG)
- Amino acids/protein
- Immunoglobulins
- Probiotics and prebiotics
- Saccharomyces boulardii
- Digestive enzymes
- Marshmallow root
- Slippery Elm
- Boswellia
- DGL
- Pectin
- Aloe vera
- Quercetin
- Dietary interventions, such as gluten free (published, peer reviewed studies show that gluten triggers leaky gut), dairy free (once leaky gut is present, casein, one of the proteins in dairy, is very hard to digest)
How I Heal Leaky Gut in 9 Easy Steps
I have taken the protocols that I’ve curated over 20 years in practice and shared them with our Functional Medicine Shop membership. You’ll find the exact brands and dosages in the FREE member section. Simply join Functional Medicine Shop for free (no hidden fees or membership upgrades, always free) AND enjoy a steep lifetime discount on all the professional lines we carry now and always!
Enjoying this content? Sign up for updates... It's FREE!